
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on understanding where accumulated amortization goes on the balance sheet. As an essential element of financial reporting, the balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given point in time. One crucial aspect of the balance sheet is capturing the amortization of intangible assets.
- When depreciated, the value of the asset is regarded as business expenses over its useful life, this is deducted from the tax return of the business.
- When this account balance increases, it will decrease the assets’ net book value on balance sheet.
- When evaluating an organization’s financial health, one must scrutinize the carrying value of its intangible assets.
- The ROU expense rises over time because the interest expense on the lease liability balance decreases.
- Then, use a combination of formulas and formatting to create the table.
Errors in Reconciliation Costing You? AI Can Fix That!

Therefore, the annual amortization expense will be $10,000 per year. This entry ensures that the expense is recognized over time, matching the asset’s consumption to the corresponding periods. In this method, the amortization expense is directly linked to the asset’s actual usage or output.
Is Amortization an Expense?

In Canada, the petty cash amortization of intangible assets is governed by International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE). Similar to IFRS 16, GASB 87 uses a single-model approach and classifies all leases as finance leases. GASB 87 also requires the lessee to recognize an intangible right-to-use lease asset, referred to as a lease asset, in conjunction with a lease liability.
Browse by type
- In other words, ASC 842 continues to distinguish between operating leases and finance leases with each lease classification requiring a capitalized ROU asset.
- In the context of loans, accumulated amortization is used to refer to the gradual repayment of a loan over a set period of time.
- For business owners, investors, or anyone curious about balance sheets, grasping this concept can reveal how a company manages its resources and preps for the future.
- Regardless of the methodology employed, it is critical to comprehend the utility of the intangible asset, its residual value, and its impact on actual production and distribution costs.
- These leases are capitalized and presented on the balance sheet as both assets and liabilities, unless subject to any of the exemptions prescribed by the standard.
You can also check out this video for other related resources when entering personal expenses in QuickBooks. I am transferring to online from a very old version of Debt to Asset Ratio QB and need to enter all my opening balances for the categories I had in that system. Ie Computer Equipment with sub categories of Cost and Accumulated depreciation.
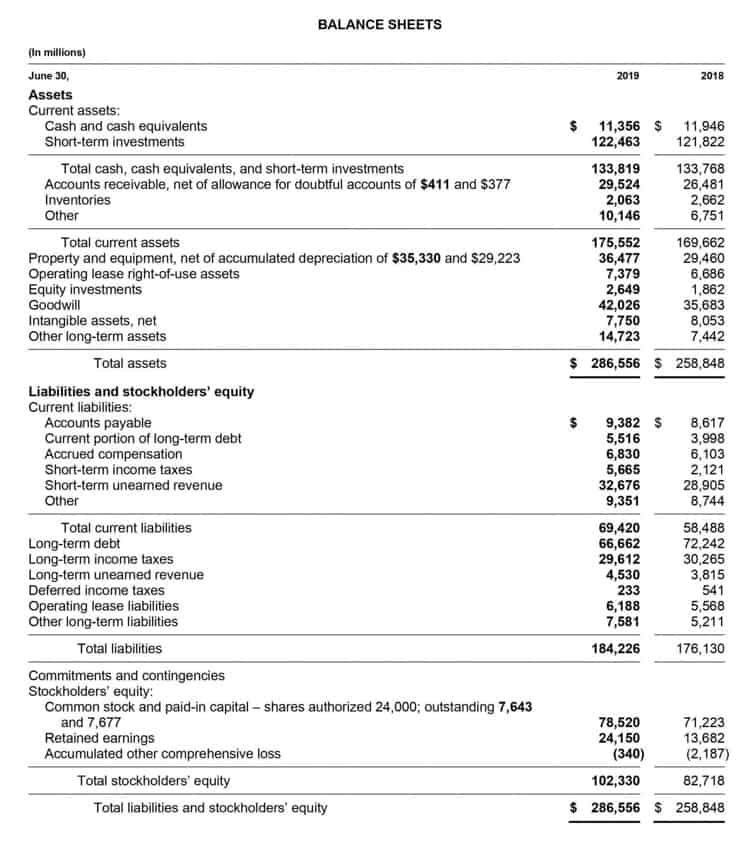
It represents the is accumulated amortization an asset period during which the asset is expected to generate economic benefits. For some assets, such as patents, the useful life is defined by legal terms, while for others, it may depend on market conditions or technological advancements. The rise in the value and importance of intangible assets might well be the biggest change experienced in the reporting of businesses over the last 30 years. The sudden growth of Internet and technology companies like Microsoft and Yahoo! has focused attention on the significance of ideas and innovation for achieving profits. Accumulated Amortization refers to the total sum of periodic amortization expenses related to an intangible asset since the asset was acquired. For companies to record amortization expenses, it is necessary to have some specific amounts.
Credit Cloud
Accumulated amortization is an important accounting concept that helps businesses keep track of the reduction in the value of their intangible assets. It is the total amount of amortization expenses that have been charged against an intangible asset from the date of its acquisition to the present time. The role of accumulated amortization is to reduce the carrying value of an intangible asset on the balance sheet, which reflects the asset’s current value. Accumulated Amortization refers to the total amount of expenses that a business has incurred over time for intangible assets, such as patents, copyrights, or business franchises, that are amortized.

Prepaid expense amortization is a method of accounting for a prepaid expense’s consumption over time. On the company’s balance sheet, this allocation is reflected as a prepayment in a current account. As is usual in the sector, accumulated amortization is frequently shown as a distinct item on the balance sheet. Another way to look at it is to think of it as a contra asset account. The goal of amortization is to reduce the value of a debt or intangible asset over time.






